

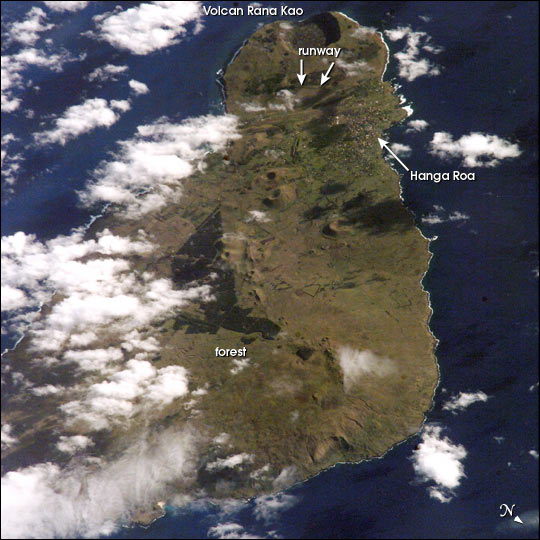
On September 25, 2002, astronauts aboard the International Space Station viewed Easter Island, one of the most remote locations on Earth. Easter Island is more than 2000 miles from the closest populations on Tahiti and Chile—even more remote than astronauts orbiting at 210 n.mi. above the Earth. The island is less than 15 miles long and, until now, has been a photographic challenge for astronauts on space missions.
Although not visible here, Easter Island is perhaps most famous for the giant stone monoliths, known as Moai, that have been placed along the coastline. Archaeologists believe the island was discovered and colonized by Polynesians at about 400 AD. Subsequently, a unique culture developed. The human population grew to levels that could not be sustained by the island. A civil war resulted, and the island’s deforestation and ecosystem collapse was nearly complete. Today, a new forest (primarily eucalyptus) has been established in the center of the island (dark green).
The geography of the island is dominated by volcanic landforms, including the large crater Rana Kao at the southwest end of the island and a line of cinder cones that stretch north from the central mountain. A final feature (difficult to see) is the very long runway (Chile’s longest) near Rana Kao. The airport serves as an emergency landing site for the Space Shuttle.
For additional information visit the Easter Island Home Page.
Astronaut photograph ISS005-E-15458 was provided by the Earth Sciences and Image Analysis Laboratory at Johnson Space Center. Additional images taken by astronauts and cosmonauts can be viewed at the NASA-JSC Gateway to Astronaut Photography of Earth.